Web Japan > Trends in Japan > Tech & Life > Ever-Expanding Uses of Dry Cell Batteries, Originally from Japan!
Ever-Expanding Uses of Dry Cell Batteries,
Originally from Japan!
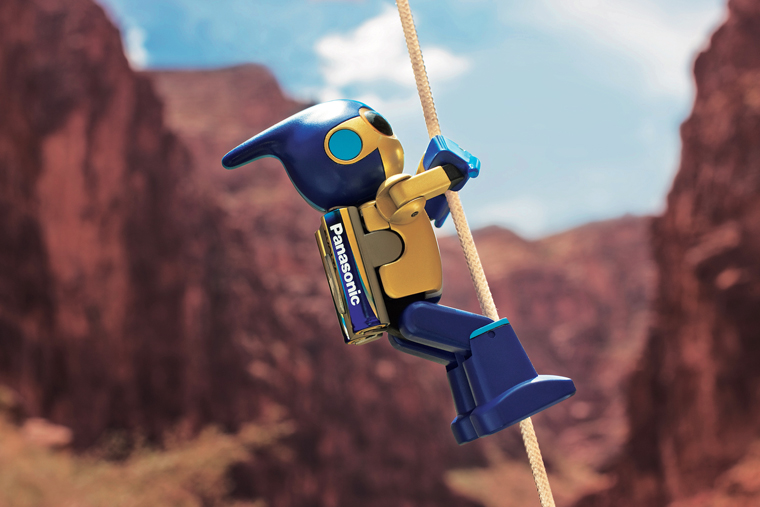

The EVOLTA Challenge was started by a Japanese company in 2008. "EVOLTA" is the product name of a dry cell battery. The challenge in May 2008 was to climb up a Grand Canyon cliff. A robot powered by 2 batteries completed the challenge by reaching the summit on its sixth attempt. © Panasonic Corporation
Dry cell batteries are essential to our lives today. People put them in TV remote controllers, flashlights and other electronic gadgets that are often used without thought in daily life. Did you know that the first person in the world to successfully invent a dry cell was actually a Japanese engineer?
People Flying on Battery Power? An Unprecedented Challenge!

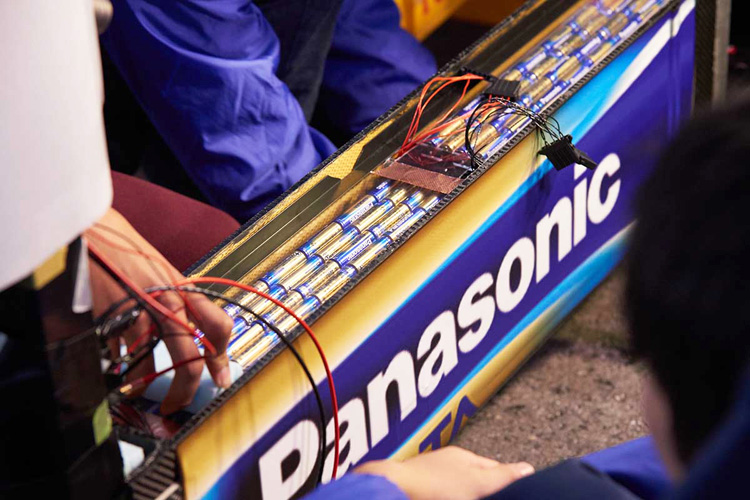
One of the Guinness world records was set in the "Railway Track Run" challenge in 2015. A train powered by 600 D batteries traveled 22.615 km. © Panasonic Corporation
The battery was invented by an Italian named Alessandro Volta in 1800, which was the start of the advancement of battery research around the world. In 1885, Sakizo Yai was the Japanese engineer who invented the world's first dry cell battery. At a time when liquid batteries were in the mainstream, his successful invention came about from his days and nights devoted to research on this easy-to-handle battery. Unfortunately, he delayed filing a patent application. Carl Gassner from Germany is historically credited as the inventor of the dry cell battery.
A lot of time has passed since then. Lately, researchers in Japan have begun looking into new uses for dry cell batteries. A Japanese electrical manufacturer has been tackling unique challenges to try to maximize the potential of the batteries.
All of the challenges have been packed with excitement, such as when a robot powered by only 2 batteries climbed a rope to scale a cliff in the U.S. Grand Canyon and when a train ran using 600 batteries as the sole power source. As a result, the manufacturer's product holds Guinness world records for the world's longest-lasting AA alkaline battery.
In 2016, the company took on the challenge of battery-powered crewed flight. They successfully flew about 3.5 km but unfortunately did not reach the target of 10 km. Witnesses were surprised and impressed that a plane could fly on battery power alone.
The power source of the dry-cell battery plane was 640 AA batteries. There were so many batteries packed in the undercarriage of the plane. © Panasonic Corporation
A Water Battery That Runs on Soda or Coffee?
Japanese-made dry cell batteries have evolved in interesting ways that may surprise you. Are these newer batteries still dry cell batteries? Let's look at a water battery, which is more than just another dry cell battery. The product was invented in Japan because it is a country that often experiences disasters, including earthquakes and typhoons. The water battery generates power from the liquid poured into the battery case. Its strong point is that it can generate power not only from water but also from a beverage (such as soda or coffee) or even spit or urine. Water is not always at hand in times of disaster or other emergencies. At such times, the battery is very helpful because it can generate power as long as there is some sort of liquid.

You can use the NoPoPo water battery like a dry cell battery by pouring water into it with the supplied dropper. © Nakabayashi Co., Ltd. (Manufacturer: Aqua Power System Japan)

A water battery added to outdoor goods not only eliminates the need to prepare a battery for every occasion but also makes it easier to separate garbage.
Another good point is that the water battery has a long shelf life. While a normal dry cell battery reaches the end of its life in 2 to 3 years, an unused water battery is surprisingly durable with a life of up to almost 20 years. In addition, the battery does not contain harmful substances, so it can be discarded as ordinary waste.
Batteries Making Magic in Ordinary Toys

The MaBeee is a device that can control a battery-operated gadget. This item has drastically changed the way that dry cell batteries have been used up to now. © Novars Inc.
In recent years, we have seen global advances in IoT (Internet of Things), which connects various things to the Internet. Dry cell batteries are, of course, no exception. Not long ago, a manufacturer in Japan attracted attention with the development of a battery-type IoT product that allows the user to manipulate a battery-operated gadget from a smartphone.
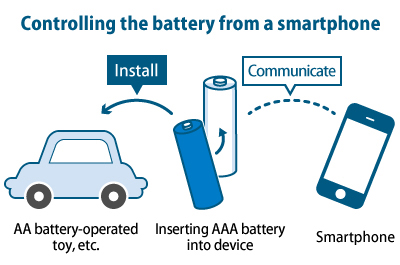
With the AA battery-shaped MaBeee, you can perform variety of operations by controlling power through a dedicated smartphone app. © Novars Inc.
This product is very easy to use. Just put a dry cell battery into the special battery case, and install it in a battery-operated toy or electronic good. The smartphone that has the dedicated app will wirelessly communicate with the battery so that you can operate the machinery from the app.

After putting the MaBeee into a favorite toy train, you can adjust the speed of the train from a smartphone, like with a remote controller. © Novars Inc.
What is interesting about this app is the various choices of action corresponding to how the smartphone is handled, such as tilting, shaking or speech input. For example, choose Tilt mode to change the battery power according to the tilt angle of the smartphone. You can, in this mode, gradually adjust LED brightness or freely adjust the speed of a toy train. As another example, suppose that you install the device in a mini 4WD remote control vehicle and choose Speech mode. Then, when you speak to the smartphone, the mini 4WD vehicle will approach you or change its speed according to the volume of your voice.
Insert the MaBeee in an automatic toothbrush and choose Clock mode to measure the tooth brushing time. Children who do not like brushing their teeth can have fun with this application, which has been well received. © Novars Inc.
With the range of play increased in this way, this dry cell battery is very popular with children. The maker has received comments from the fathers and mothers of children who have actually used it. One said, "The good point is that we don't have to buy new toys but instead can have fun with something already at home." Another said, "I like to use it for my son's crafts to play together with him."
More than 130 years have passed since the dry cell battery was invented in Japan, but the great possibilities contained in its small form are still largely unknown. In the near future, as the research continues, we may be able to do lots more, which will drastically change our current way of life.




